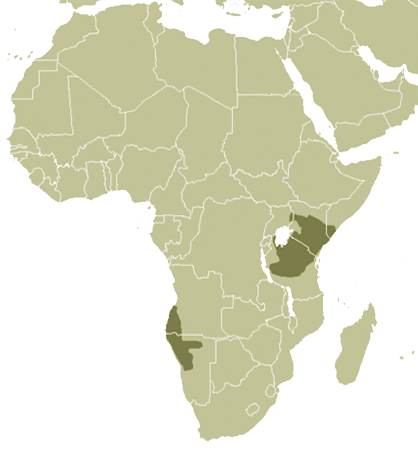
Range
Africa
African
Dik Dik
Madoqua kirkii
A dik-dik is the name for any of four species of small antelope in the genus Madoqua that live in the bushlands of eastern and southern Africa. Dik-diks stand about 30–40 centimetres (12–15.5 in) at the shoulder, are 50–70 cm (19.5–27.5 in) long, weigh 3–6 kilograms (6.6–13.2 lb) and can live for up to 10 years. Dik-diks are named for the alarm calls of the females. In addition to the females’ alarm call, both the male and female make a shrill, whistling sound. These calls may alert other animals to predators.
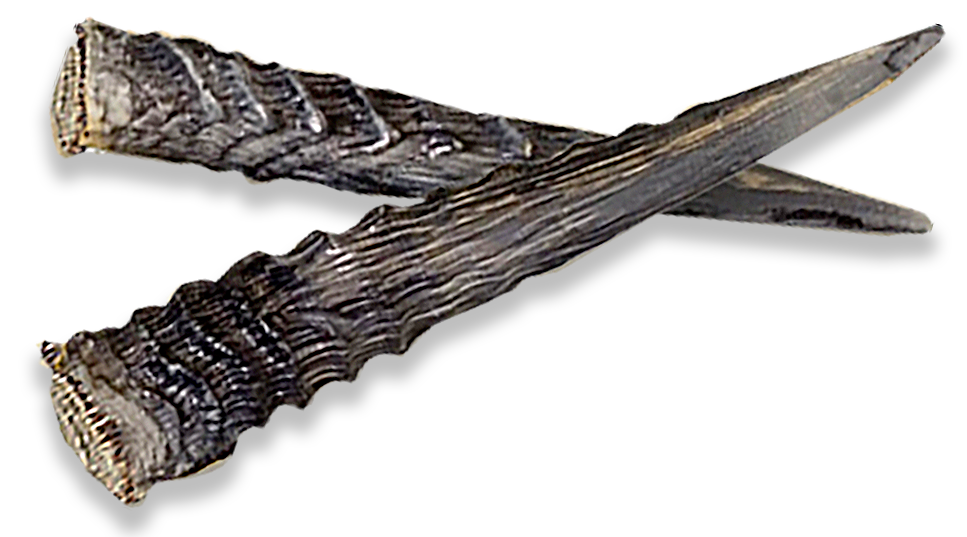
Female dik-diks are somewhat larger than males. The males have horns, which are small (about 7.6 centimetres or 3 in), slanted backwards and longitudinally grooved. The hair on the crown forms an upright tuft that sometimes partially conceals the short, ribbed horns of the male. The upper body is gray-brown, while the lower parts of the body, including the legs, belly, crest, and flanks, are tan. A bare black spot below the inside corner of each eye contains a preorbital gland that produces a dark, sticky secretion. Dik-diks insert grass stems and twigs into the gland to scent-mark their territories.
Apparently to prevent overheating, dik-diks have elongated snouts with bellows-like muscles through which blood is pumped. Airflow and subsequent evaporation cools this blood before it is recirculated to the body. However, this panting is only implemented in extreme conditions; dik-diks can tolerate air temperatures of up to 40 °C (104 °F).
Dik-dik are herbivorous and their diets consist mainly of foliage, fruits, shoots, and berries. Due to their adaptations, dik-diks are water-independent and rely on vegetation as a source of water. Kirk’s dik-diks are concentrate selectors, feeding selectively on dicotyledonous plants that can be rapidly fermented and digested. This includes leaves and fruit high in nutrients and water, but low in fiber and cellulose. Grasses are only consumed when they are germinating and Kirk’s dik-diks have stomach capacities and mass that consist of 8.5–10.0% of body mass when full and 2.2% when empty”.They consume roughly 3.8% of their body mass daily.

Meaning of the Name
The dik-dik’s name is derived from its call. When they feel threatened, dik-diks lie low to prevent detection. If they are discovered, they run in a swift, zigzag-like pattern until they reach refuge in a nearby thicket. During this ‘flight’, they emit trumpet-like “zik-zik” calls to raise an alarm or to harass predators and publicize the presence of a mated pair.