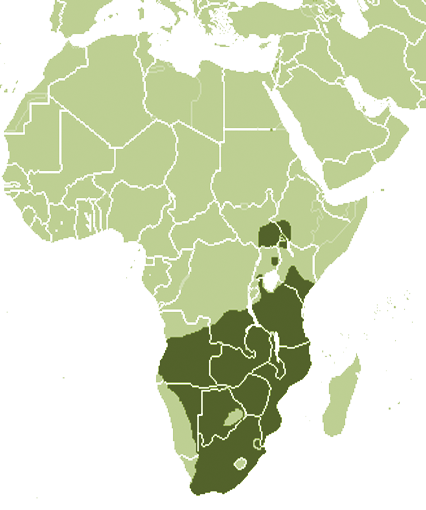
Range
Africa
Africa
Eland
Taurotragus oryx
The common eland (Taurotragus oryx), also known as the southern eland or eland antelope, is a savannah and plains antelope found in East and Southern Africa. It is a species of the family Bovidae and genus Taurotragus. An adult male is around 1.6 metres (5′) tall at the shoulder (females are 20 centimetres (8″) shorter) and can weigh up to 942 kg (2,077 lb) with an average of 500–600 kg (1,100–1,300 lb), 340–445 kg (750–981 lb) for females). It is the second largest antelope in the world, being slightly smaller on average than the giant eland. It was scientifically described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1766.
Mainly an herbivore, its diet is primarily grasses and leaves. Common elands form herds of up to 500 animals, but are not territorial. The common eland prefers habitats with a wide variety of flowering plants such as savannah, woodlands, and open and montane grasslands; it avoids dense forests. It uses loud barks, visual and postural movements and the flehmen response to communicate and warn others of danger. The common eland is used by humans for leather, meat, and rich, nutritious milk, and has been domesticated in many areas.
It is native to Angola, Botswana, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe but is no longer present in Burundi. While the common eland’s population is decreasing, it is classified as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
It is native to Angola, Botswana, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, Rwanda, South Africa, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe but is no longer present in Burundi. While the common eland’s population is decreasing, it is classified as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
The common eland is sometimes farmed and hunted for its meat, and in some cases can be better used than cattle because it is more suited to African climates. This has led to some Southern African farmers switching from cattle to eland. Common elands are also pictured as supporters in the coat of arms of Grootfontein, Namibia.
Eland Facts
The common eland is better adapted than cattle to the African environment, and is easily domesticated. It has been farmed for its meat and milk in both South Africa and Russia. A female can produce up to 7kg of milk per day, which is richer in fat than cow milk.